Prototypeパターン Java
デザインパターンの一つであるPrototypeパターンについて記述する。
なぜPrototypeパターン?
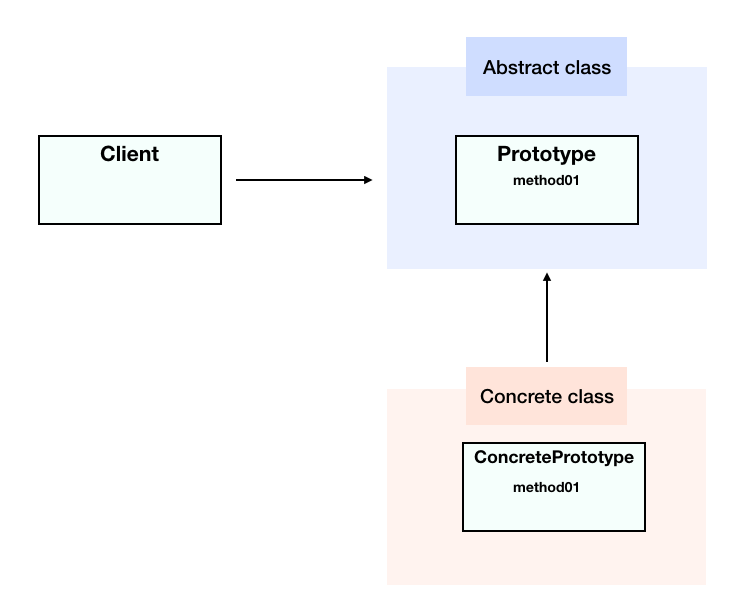
原型となるインスタンスを用いて、他のクラスを生成し、新しいインスタンスを作成するパターンのことをPrototypeパターン。Prototypeは、スーパークラスであるObjectクラスで定義されているcloneメソッドを用いてインスタンスの作成をする。
Protoypeパターンにおける良い点は以下が考えられる。
- いくつかの似たクラスのインスタンスが存在する場合、クラスを分ける必要がなく実装可能
- クラス内処理でのインスタンス生成が難しい場合、インスタンス生成難易度が低い
サンプルコード
Prototypeインターフェースの実装。
Cloneableを継承する。
1 | public interface Prototype extends Cloneable { |
ConcretePrototypeクラス。Prototypeの実装クラスの実装。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35public class ConcretePrototype implements Prototype {
private char val;
public ConcretePrototype(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
public void greet(String s) {
int length = s.getBytes().length;
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.println(val);
}
System.out.print(" ["+s+"] ");
for(int i=0; i<length; ++i) {
System.out.print(val);
}
System.out.println("");
}
public Prototype createClone() {
Prototype p = null;
try {
p = (Prototype) clone();
} catch(CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return p;
}
}
Prototypeを利用するクライアントクラスの実装。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public class Client {
private HashMap<String, Prototype> hash = new HashMap<String, Prototype>();
public void register(String key, Prototype proto) {
hash.put(key, proto);
}
public Prototype create(String key) {
return hash.get(key).createClone();
}
}
Mainクラスの実装.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15public class Main {
public static void main(String args []) {
Client client = new Client();
client.register("typeA", new ConcretePrototype('A'));
client.register("typeB", new ConcretePrototype('B'));
client.register("typeC", new ConcretePrototype('C'));
Prototype p1 = client.create("typeA");
Prototype p2 = client.create("typeB");
Prototype p3 = client.create("typeC");
p1.greet("hi");
p2.greet("hi");
p3.greet("hi");
}
}