Iteratorパターン Java
デザインパターンの一つであるIteratorパターンについて記述する。
Iteratorパターンとは?
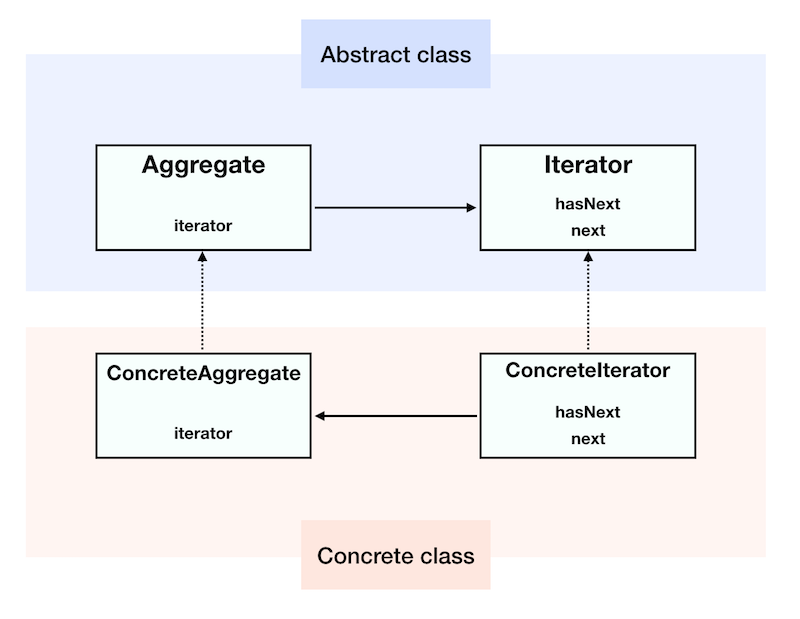
Iteratorはループ処理で利用する。
シリアルに要素アクセスするコレクション。
例えば、Javaオブジェクトを保持するリストがあったとし、そのリストからシリアルに取り出したいケースに利用するパターン。
サンプルコード
人の構造体を持つ具象クラスを実装。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public int getAge() {
this.age;
}
}
|
Personクラスを複数保持するPersonListクラスを実装。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class PersonList implements Aggregate {
private Person[] persons;
private int last = 0;
public PersonList() {}
public PersonList(int count) {
this.person = new Person[count];
}
public void add(Person person) {
persons[last] = person;
last++;
}
public Person getPersonAt(int index) {
return persons[index];
}
public int getLength() {
return this.last;
}
public Iterator iterator() {
return new PersonIterator(this);
}
}
|
PersonのIteratorクラス。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class PersonIterator implements Iterator {
private PersonList personList;
private int index;
public PersonIterator(PersonList personList) {
this.personList = personList;
this.index = 0;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
if (index < personList.getLength()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public Object next() {
Person person = personList.getPersonAt(index);
index++;
return person;
}
}
|
Mainクラス。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class Main {
public static void main(String [] args) {
PersonList personList = new PersonList(4);
personList.add(new Person("test1"));
personList.add(new Person("test2"));
personList.add(new Person("test3"));
personList.add(new Person("test4"));
Iterator iterator = personList.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Person person = (Person) iterator.next();
System.out.println(person.getName());
}
}
}
|
